Role in the pipeline
StørmBehaviour models event-level state transitions across identities, processes, and control operations. It evaluates explicit behavioural invariants and emits structured evidence for StørmDecision; it does not make enforcement decisions.

Contract: events → behavioural state → signals
State updates and invariant signals for decisioning.
Inputs
Events, deterministic features, and current behavioural state.
Processing
State updates, invariant evaluation, and sequence tracking.
Outputs
Invariant results and behavioural signals to StørmDecision.
How it works
Three steps from baseline to enforcement signal.
Learn baseline
Establish baselines within bounded windows and roles.
Update state per event
Update behavioural state and evaluate invariants on each event.
Emit + seal signal
Send signals to StørmDecision and seal metadata in StørmVault.
Interfaces
- Inputs: canonical events and deterministic features.
- Outputs: behavioural state summaries and risk signals.
- Contracts: state versioning and baseline windows.
- Failure semantics: cold-start handling with bounded defaults.
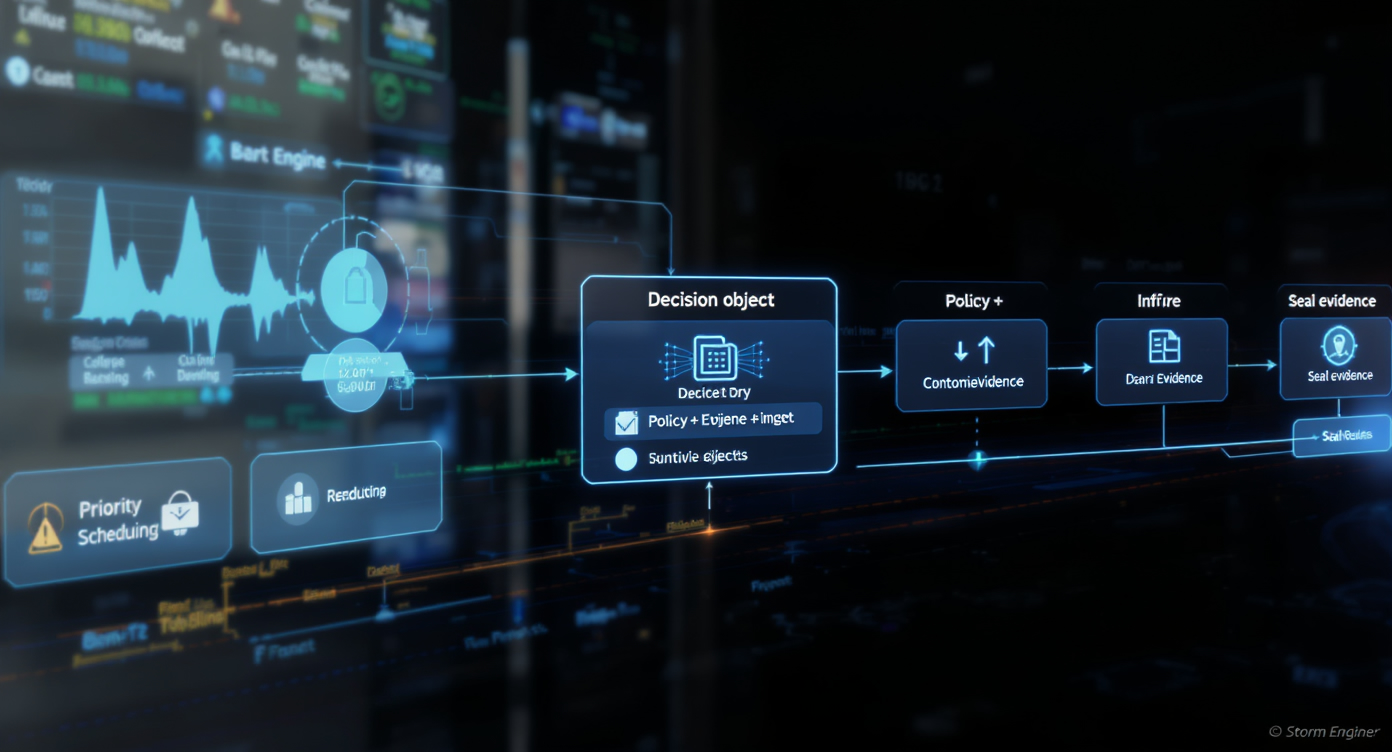
State machines for behavioural truth.
StørmBehaviour tracks sequences and transitions, not just anomaly scores.
It binds behavioural evidence to policy clauses for explainable decisions.
Outputs are structured and auditable, ready for fusion in StørmDecision.
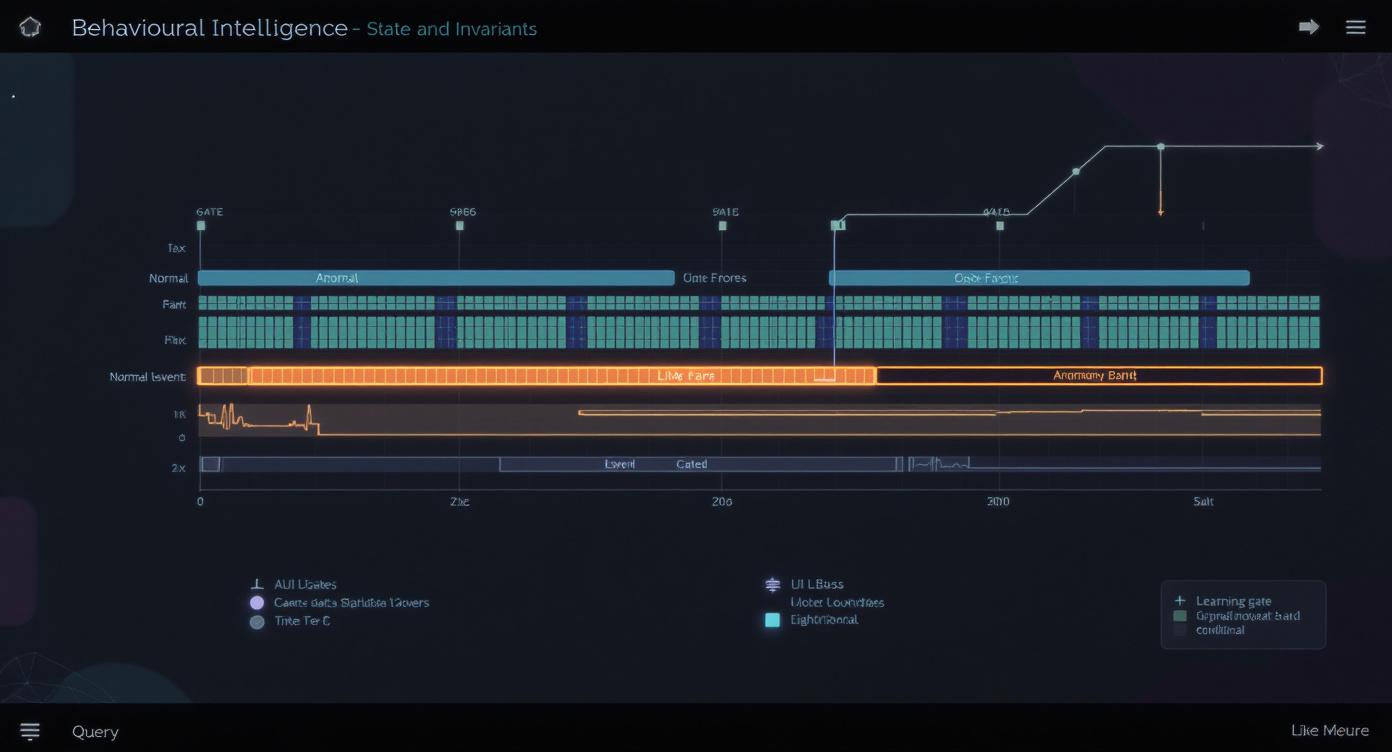
Bounded behavioural contracts.
- Bounded state windows per entity, zone, and mission mode.
- Explicit invariants with rationale bound to policy clauses.
- Trust-gated learning prevents poisoning and drift.
- Outputs include sequences, invariant results, and evidence provenance.
- Evidence artefacts are sealed in StørmVault.
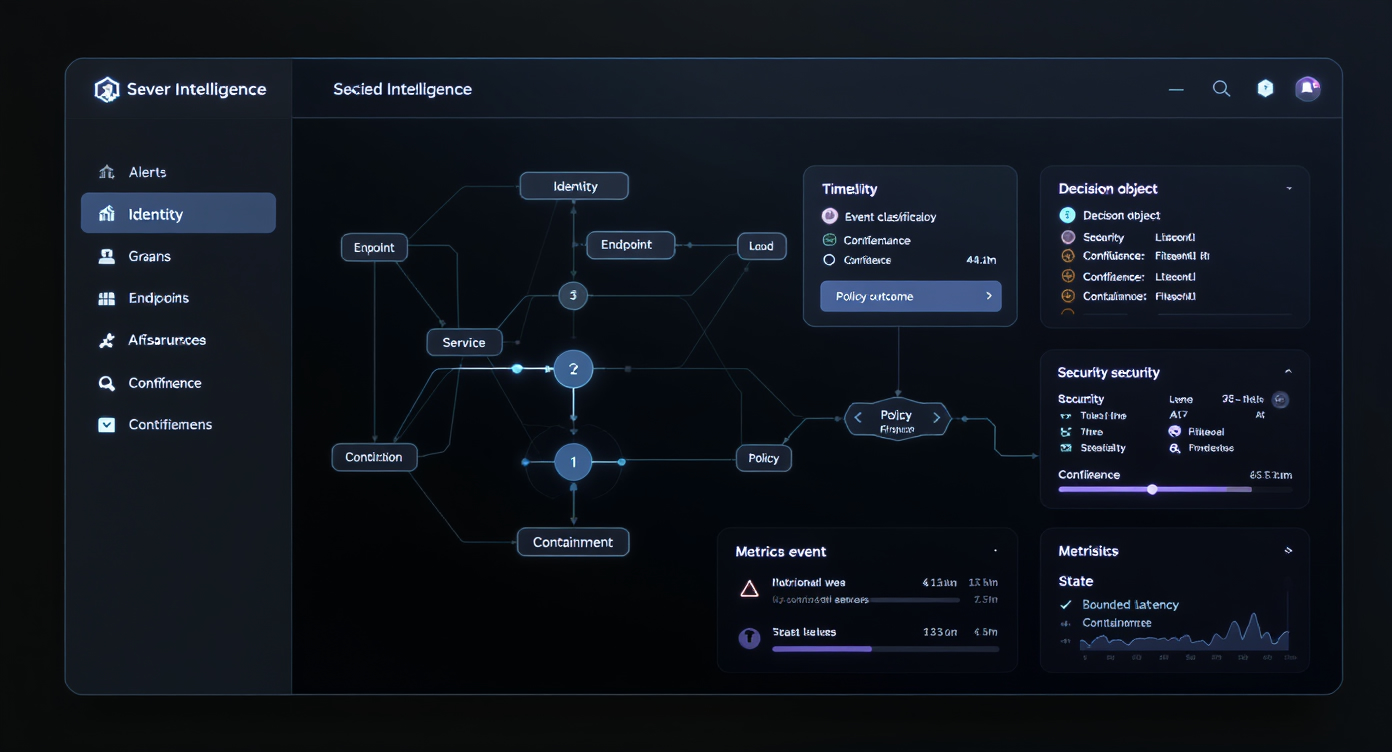
Behavioural signals
- Sequence breaks and unexpected transitions.
- Cadence shifts and timing anomalies.
- Privilege anomalies across roles and sessions.
- Cross-domain inconsistencies between identities and assets.
Controls for signal quality
- Segmented baselines by role, zone, and mission mode.
- Thresholds and hysteresis tuned to policy context.
- Trust-gated learning to prevent baseline poisoning.
- Explainable features for every invariant evaluation.

Capabilities
Behavioural analysis with bounded state and explainability hooks.
Event-level state transitions
Models sequences, timing, and state transitions with bounded state windows per entity and mode. So what: behaviour remains bounded and interpretable.
Explicit constraints with rationale
Invariants define allowed transitions and rhythms, emit rationale per evaluation, and bind directly to policy clauses. So what: decisions stay explainable and policy-bound.
Do not learn from compromised data
Learning updates are gated by cryptographic trust state and policy, blocking degraded or quarantined sources. So what: baselines resist poisoning.

Context-aware behavior profiles
Baselines vary by role, zone, and mission mode to reduce noise and preserve explainability. So what: anomalies remain contextual and defensible.